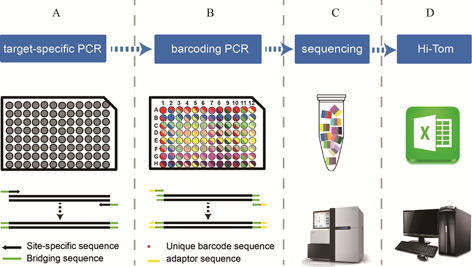
2. Distribution of primer combinations in a 96-hole plate.
The target site should be within 10-100 bp of the forward or reverse primer. The bridging sequence (5’-ggagtgagtacggtgtgc-3’) is added at the 5’ end of the forward specific primer, and another bridging sequence (5’-gagttggatgctggatgg-3’) is added at the 5’ end of the reverse specific primer.
2. Target-specific PCR.
The specific target fragment is amplified using the target specific PCR primers mentioned above (No dye).
The PCR products are detected by agarose gel electrophoresis to ensure that the desired fragment are successfully amplified.
3. Barcoding PCR using preassmbled mix.
PCR reaction system:
ddH2O 9.0 µL
Hi-TOM Mix 10 µL
The first round of PCR products 1.0 µL
Total volume 20.0 µL
PCR cycle set-up:
1 94℃,2 min;
2 94℃,30 sec;
3 57℃,30 sec;
4 72℃,1 kb/min;
Go to step 2 for 33 times
5 72℃,5 min
The products are detected by agarose gel electrophoresis after the PCR. The second round of PCR products should be 100 bp longer than the first round of PCR products.The second round of PCR products are mixed, and the mixture (200 µL) are detected and purified. The high-throughput sequencing (NGS) samples should with a concentration greater than 0.8 ng /µL, total amount more than 30 ng and volume more than 10ul. Samples of different target sites can be mixed together. For 960 PCR reactions, reliable results can be obtained with 1 Gb sequencing data.
4. Tracking the mutation using Hi-TOM online tool.
The first step is entering a working directory (note that filenames cannot include spaces) to prevent conflicts with other tasks. The second step is click the ‘Choose File’ buttons to upload the forward reads (named_1.fq.gz) and reverse reads (named_2.fq.gz). The third step is to upload the reference sequence. If multiple targets are analyzed simultaneously, the reference sequences of different targets are sorted into TXT format and submitted. Then, the submit button is clicked and data are uploaded to the server automatically and directly input into the analysis process. 1 Gb data needs about 8 minutes to complete the analysis.
Presentation and interpretation of the results
example-Rice-edited-gene1-Genotype
example-Rice-edited-gene1-Sequence
2. The genotype file gives the genotype of each sample of the 96 hole plate.
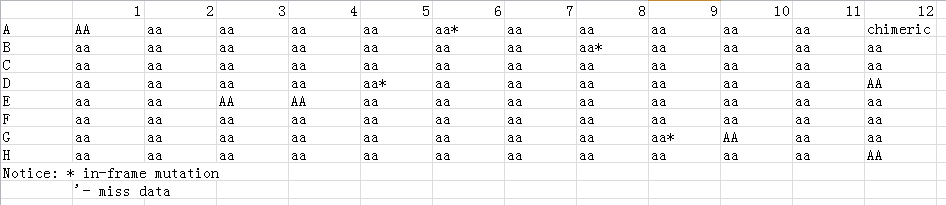
3. The Sequence file displays detail mutation information of each material.

Data Interpretation:
It is recommended that the data of Ratio>=10% and Reads>=100 can be trusted. In the Variation_type column, numbers represent the number of mutated bases, and letters represent mutations. For example, 1D represents 1 base deletions, and 1I represents 1 base insertions. 1S represents 1 SNP, and the Variation column shows the missing or inserted sequence. The lowercase letters in the Reads_seq column is the starting position of the mutation position.
Please cite the following article if you found Hi-TOM helpful in your work:
Liu Q, Wang C, Jiao X, Zhang H, Song L, Li Y, Gao C, Wang K. 2018. Hi-TOM: a platform for high-throughput tracking of mutations induced by CRISPR/Cas systems. bioRxiv (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/235903 )